Air compressor is a mechanical equipment that compresses gas volume, increases gas pressure, and transports gas. As a consumption product of power energy, its application range and industry are very wide.

According to the working principle, air compressors are divided into volume type and speed type. Volume type can be divided into three types: piston type, screw type, and sliding plate type; The speed type can be divided into two types: centrifugal and axial flow. This article discusses the working principles, advantages, disadvantages, and application scope of six common air compressors.
1 piston compressor
The work of a piston compressor is achieved by continuously changing the working volume of the cylinder, air valve, and piston that moves back and forth in the cylinder.
If the volume loss and energy loss (i.e. ideal working process) in the actual operation of a piston compressor are not considered, the work completed by the crankshaft of the piston compressor after each rotation can be divided into suction, compression, and exhaust processes.
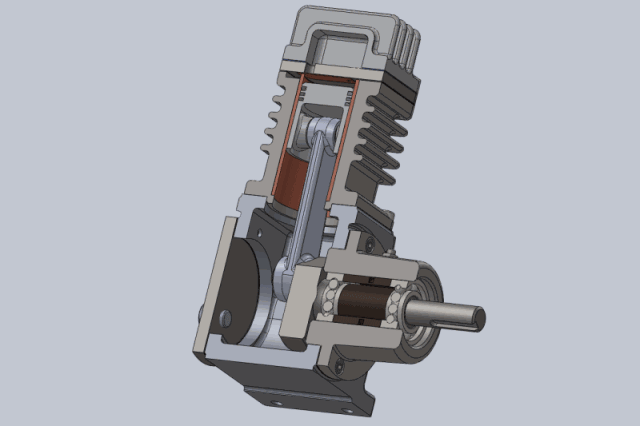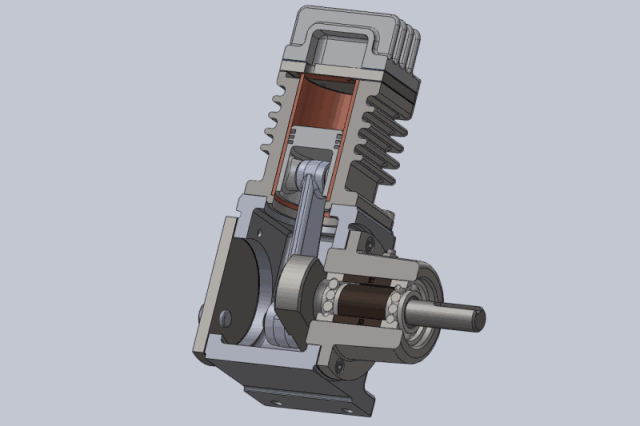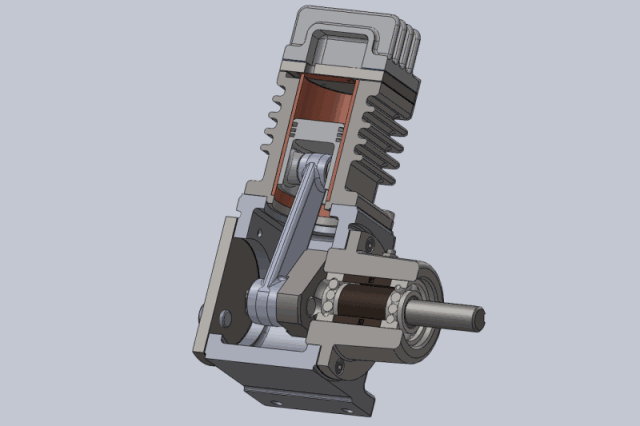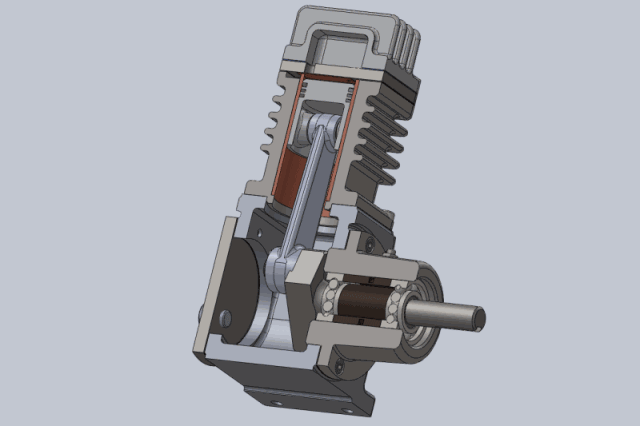
Working principle of piston compressor:
Compression process: The piston moves upwards from the bottom dead center, the suction and exhaust valves are closed, and the gas is compressed in a closed cylinder. As the cylinder volume gradually decreases, the pressure and temperature gradually increase until the gas pressure in the cylinder is equal to the exhaust pressure.
Exhaust process: The piston continues to move upwards, causing the gas pressure in the cylinder to be greater than the exhaust pressure. The exhaust valve opens, and the gas in the cylinder is pushed out of the cylinder under equal pressure by the piston and enters the exhaust pipeline until the piston moves to the top dead center. At this point, due to the force of the exhaust valve spring and the gravity of the valve plate itself, the exhaust valve closes and the exhaust ends.
Advantages and disadvantages: The piston type air compressor is cheap, easy to maintain and cheap, but it is prone to damage and has high noise.
2 screw compressor
Screw compressors are divided into single screw compressors and double screw compressors.
Working principle of screw compressor:
The cylinder of the screw compressor is equipped with a pair of helical male and female rotors that mesh with each other. Both rotors have several concave teeth and rotate in opposite directions to each other.
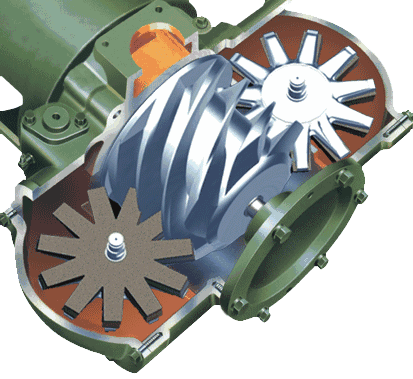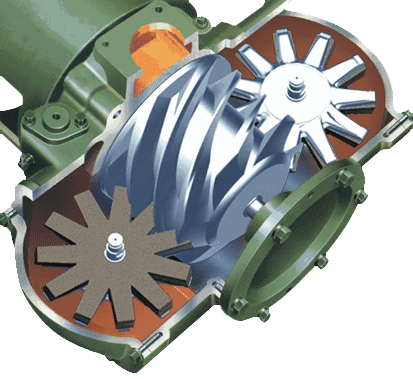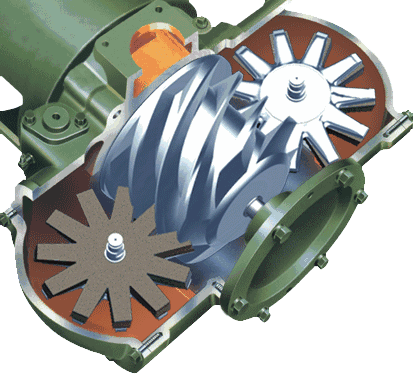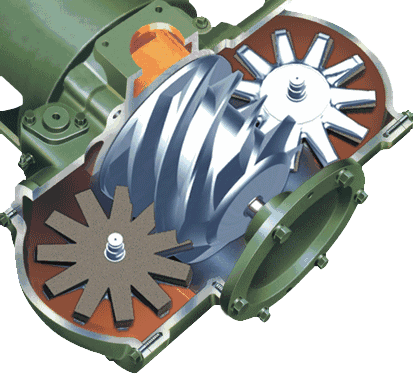
The gap between the rotors and between the casing and rotor is only 5-10 threads. The main rotor (also known as the male or convex rotor) is driven by an engine or an electric motor (mostly an electric motor), while the other rotor (also known as the female or concave rotor) is driven by an oil film formed by the main rotor through oil injection, or by synchronous gears at the main rotor end and the concave rotor end.
Advantages and disadvantages: High gas production, low noise, high reliability, but relatively high cost, cannot be used in ultra-high pressure situations.
3 centrifugal compressors
A centrifugal compressor, also known as a turbine compressor, is mainly used to compress gases and is mainly composed of a rotor and a stator.
The rotor includes an impeller and a shaft, on which there are blades, balance plates, and a portion of shaft seals; The main body of the stator is the cylinder, and there are also devices such as a diffuser, bend, reflux device, intake pipe, exhaust pipe, etc.
Working principle of centrifugal compressor:
When the impeller rotates at high speed, the gas rotates with it. Under the action of centrifugal force, the gas is thrown into the rear diffuser, forming a vacuum zone at the impeller. At this time, fresh gas from the outside enters the impeller.
The impeller rotates continuously, and the gas is constantly sucked in and thrown out, thereby maintaining a continuous flow of gas.
Main advantages: large and continuous gas transmission, smooth operation; The unit has a small external size, light weight, and a small footprint; The equipment has fewer vulnerable components, a long service life, and a small maintenance workload; Due to its high speed, it can be directly driven by a steam turbine, which is relatively safe and easy to achieve automatic control.
Main drawbacks: lower efficiency than axial and reciprocating compressors; The stable working condition zone is relatively narrow and there is a phenomenon of surging.
4 rotor compressor
A rotary compressor is driven by an engine or electric motor (mostly electric motor), while another rotor (also known as a female or concave rotor) is driven by an oil film formed by the main rotor through oil injection, or by synchronous gears at the main rotor end and the concave rotor end.
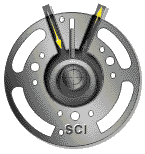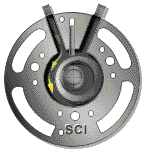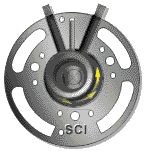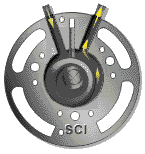
Principle of rotary compressor:
When the rotor rotates to compress lubricant+gas (referred to as oil gas mixture), the volume of the compression chamber decreases and the oil gas mixture is compressed towards the exhaust port. When the compression chamber passes through the exhaust port, the oil and gas mixture is discharged from the compressor, completing a process of suction compression exhaust.
5 axis compressor
Axial flow compressor is a large air compressor with a maximum power of 150000 KW and a displacement of 20000 cubic meters per minute. Its compressor energy efficiency ratio can reach about 90%, which is more energy-saving than centrifuges.
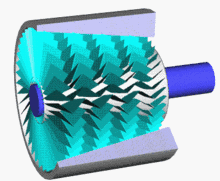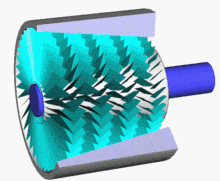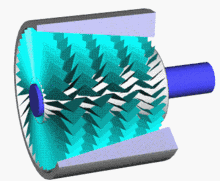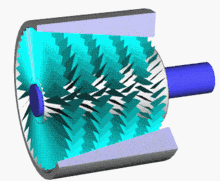
Axial flow compressors and centrifugal compressors are both speed type compressors, both referred to as turbine compressors.
Advantages: High efficiency, single machine efficiency can reach 86% -92%, 5% -10% higher than centrifugal compressors, large flow capacity per unit area, small radial size, suitable for flow rate greater than 1500m ³/ In the case of min, the single-stage pressure is relatively low, and the single-cylinder multi-stage pressure ratio can reach 11. The structure is relatively simple and easy to maintain.
6 sliding vane compressor
The sliding vane compressor is driven directly at a very low speed, and the rotor is the only continuously running component with several grooves cut along the length direction, which are inserted with sliding vanes that can slide on the oil film. The rotor rotates in the stator of the cylinder.
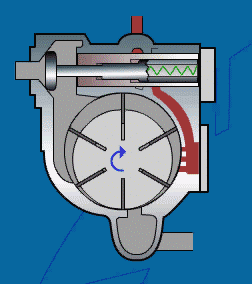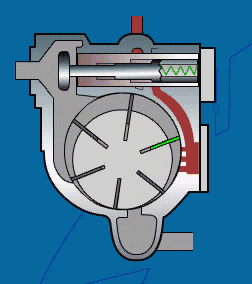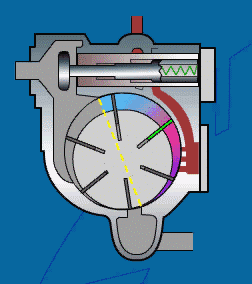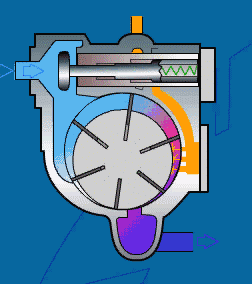
Working principle of sliding vane compressor:
The air is sucked in through a filter and a regulating proportional valve, which is mainly used to regulate the pressure chamber formed by the air cylinder rotor and sliding blades. The rotor rotates in an eccentric manner relative to the cylinder, and the valve plate is installed in the slot of the rotor. The sliding plate is pushed to the cylinder wall by centrifugal force. The efficient oil injection system can ensure the cooling of the compressor and the minimum loss of lubricant. A thin oil film formed on the cylinder wall can prevent direct contact between metal components and cause wear.
Advantages and disadvantages: Durable and requires minimal maintenance. The main disadvantage is that there is significant mechanical friction between the slide and the rotor cylinder, resulting in significant energy loss and lower efficiency.
