Using the right tools for cutting copper ensures clean and precise cuts. Copper cutting tools serve various applications, from plumbing to electrical work. These tools include pipe cutters, hacksaws, and reciprocating saws. Each tool offers unique benefits tailored to specific tasks, making the selection process crucial for achieving optimal results.
Types of Copper Cutting Tools

Manual Copper Cutting Tools
Pipe Cutters
Pipe cutters are essential for achieving clean and precise cuts in copper pipes. The tool features a sharp cutting wheel and adjustable jaws. Users place the pipe between the jaws and rotate the cutter around the pipe. This action scores the copper surface, eventually cutting through it. Pipe cutters are ideal for plumbing tasks where accuracy is crucial.
Hacksaws
Hacksaws offer versatility in cutting various materials, including copper. The tool consists of a metal frame and a replaceable blade. Users manually move the blade back and forth to cut through the copper. Hacksaws are suitable for situations where power tools are not available. The tool requires more effort but provides control over the cutting process.
Power Copper Cutting Tools
Reciprocating Saws
Reciprocating saws use a motor to move the blade rapidly back and forth. This motion allows the tool to cut through copper pipes quickly. Users can change blades to suit different materials and thicknesses. Reciprocating saws are efficient for large projects requiring multiple cuts. The tool reduces manual effort and speeds up the cutting process.
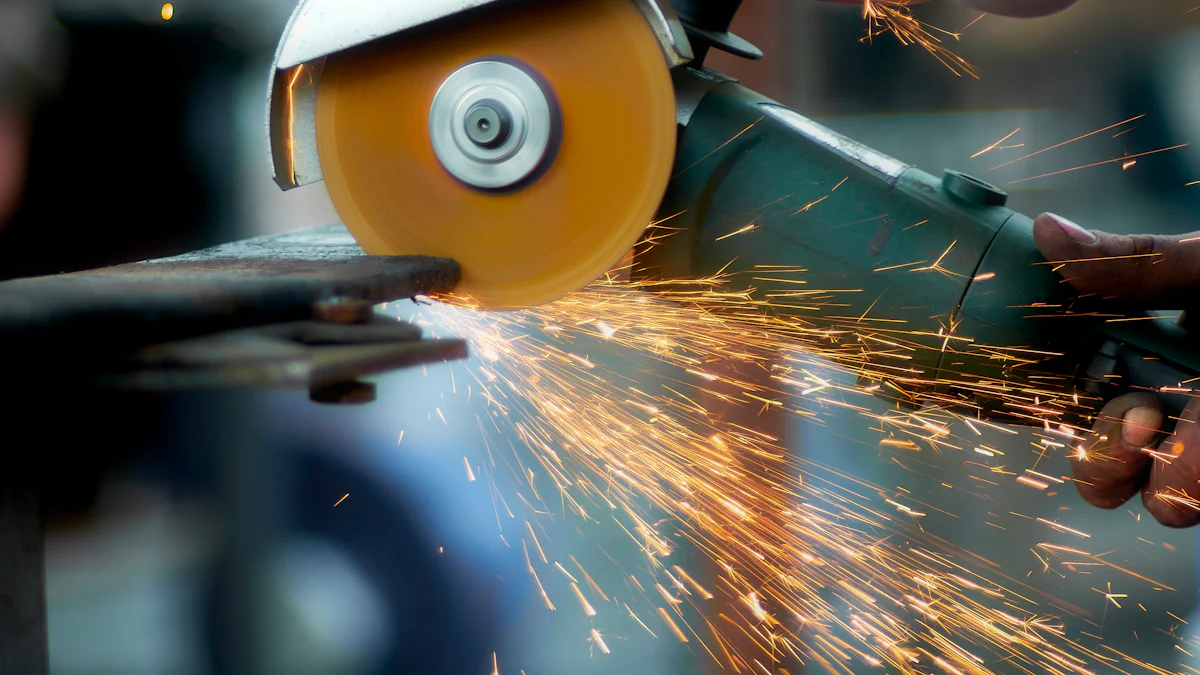
Angle Grinders
Angle grinders feature a rotating disc that can cut through various materials, including copper. Users hold the grinder at an angle to the material and guide it along the desired cut line. The tool’s high-speed rotation ensures smooth and fast cuts. Angle grinders are versatile and can handle both rough and fine cuts, depending on the disc used.
Specialized Copper Cutting Tools
Tube Cutters
Tube cutters are specifically designed for cutting copper tubing. The tool has a circular blade and a tightening mechanism. Users place the tubing in the cutter and tighten the knob to secure it. Rotating the cutter around the tubing creates a clean and precise cut. Tube cutters are commonly used in HVAC and plumbing applications.
Rotary Tools
Rotary tools offer precision in cutting and shaping copper. The tool uses various attachments, such as cutting wheels and burrs, to perform different tasks. Users can adjust the speed and choose the appropriate attachment for the job. Rotary tools are ideal for intricate work requiring detailed cuts and modifications.
How to Choose the Right Copper Cutting Tool
Consider the Material Thickness
Thin Copper Sheets
Thin copper sheets require a specific type of copper cutting tool. A rotary tool with a cutting wheel attachment works well for thin sheets. This tool allows for precise cuts and minimal material wastage. Another option includes using a hacksaw with a fine-toothed blade. This method provides control over the cutting process, ensuring clean edges.
Thick Copper Pipes
Thick copper pipes demand a more robust copper cutting tool. A pipe cutter proves effective for this task. The sharp cutting wheel and adjustable jaws of a pipe cutter score and cut through thick pipes with precision. For larger diameter pipes, a reciprocating saw offers efficiency. The motorized blade of the reciprocating saw makes quick work of thick copper pipes.
Evaluate the Cutting Precision Required
Rough Cuts
Rough cuts do not require high precision. An angle grinder serves as an excellent choice for rough cuts. The rotating disc of the angle grinder can handle various materials, including copper. This tool ensures fast and efficient cuts. A hacksaw also works for rough cuts, especially when power tools are unavailable.
Fine Cuts
Fine cuts necessitate a high level of precision. A tube cutter excels in making fine cuts on copper tubing. The circular blade of the tube cutter creates clean and precise cuts. A rotary tool with a fine cutting wheel also works well for detailed cuts. Adjusting the speed and choosing the right attachment ensures accuracy.
Assess the Work Environment
Indoor Use
Indoor use often requires quieter and less messy tools. A pipe cutter fits well for indoor tasks. This manual copper cutting tool operates quietly and produces minimal debris. A hacksaw also suits indoor environments. The manual operation of the hacksaw keeps noise levels low.
Outdoor Use
Outdoor use allows for more flexibility in tool selection. Power tools like reciprocating saws and angle grinders prove advantageous for outdoor tasks. These tools handle larger projects efficiently. The high-speed operation of these tools speeds up the cutting process, making them ideal for outdoor environments.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using Copper Cutting Tools

Preparing the Work Area
Clearing the Space
Clear the work area of any unnecessary items. Ensure that the workspace is free from clutter. A clean space reduces the risk of accidents and allows for better maneuverability. Proper lighting is also essential for visibility.
Gathering Necessary Equipment
Gather all necessary equipment before starting the project. This includes the chosen copper cutting tool, measuring tape, marker, and safety gear. Having everything within reach saves time and ensures a smooth workflow.
Safety Measures
Wearing Protective Gear
Always wear protective gear when using a copper cutting tool. Safety goggles protect the eyes from flying debris. Gloves provide a better grip and protect the hands from sharp edges. A dust mask prevents inhalation of fine particles.
Ensuring Proper Ventilation
Ensure proper ventilation in the work area. Cutting copper can produce fine particles that are harmful if inhaled. Open windows or use fans to maintain good air circulation. This practice keeps the air clean and reduces health risks.
Cutting Techniques
Marking the Cut Line
Mark the cut line on the copper material with a marker. Use a measuring tape to ensure accuracy. A clear and precise mark guides the cutting process. Double-check measurements to avoid mistakes.
Using the Tool Correctly
Use the copper cutting tool according to the manufacturer’s instructions. For a pipe cutter, place the pipe between the jaws and rotate the cutter around the pipe. Tighten the knob after each rotation until the pipe is cut. For a hacksaw, move the blade back and forth along the marked line. Maintain steady pressure to ensure a straight cut. For power tools like reciprocating saws or angle grinders, hold the tool firmly and guide it along the cut line. Follow safety protocols to prevent accidents.
Post-Cutting Procedures
Inspecting the Cut
Inspect the cut immediately after finishing. Check for any irregularities or rough edges. A clean cut ensures proper fitting and connection. Use a reamer to smooth out any burrs inside the pipe. Sandpaper can help achieve a smooth exterior edge. This step is crucial for preventing leaks in plumbing applications.
Cleaning Up
Clean up the work area after completing the cut. Remove any metal shavings or debris from the workspace. Proper disposal of waste materials maintains a safe environment. Store the copper cutting tools in their designated places. Regular cleaning and organization extend the lifespan of the tools. A tidy workspace promotes efficiency and safety for future projects.
Maintenance and Care of Copper Cutting Tools
Proper maintenance ensures the longevity and efficiency of any copper cutting tool. Regular care prevents wear and tear, ensuring tools perform optimally for each task.
Regular Cleaning
Removing Debris
Debris can accumulate on a copper cutting tool after each use. Removing debris involves brushing off metal shavings and dust. A clean tool reduces the risk of malfunction and ensures smooth operation. Use a soft brush or cloth to wipe down the tool after every project.
Lubricating Moving Parts
Lubrication keeps the moving parts of a copper cutting tool in good condition. Apply a few drops of oil to hinges, blades, and other moving components. Lubrication reduces friction and prevents rust. Regular oiling extends the lifespan of the tool and maintains its cutting efficiency.
Proper Storage
Storing in a Dry Place
Moisture can cause rust and damage to a copper cutting tool. Store tools in a dry place to prevent corrosion. A toolbox or storage cabinet with a dehumidifier works well. Keeping tools dry ensures they remain in good working condition.
Organizing Tools Neatly
Organizing tools neatly prevents damage and makes them easy to find. Use tool organizers or pegboards to keep each copper cutting tool in its place. Proper organization reduces the risk of losing parts and ensures quick access when needed.
Sharpening and Replacing Blades
When to Sharpen
Blades on a copper cutting tool need sharpening when cuts become rough or uneven. Use a sharpening stone or file to restore the blade’s edge. Regular sharpening ensures clean cuts and reduces the effort required for each task. Inspect blades regularly to determine when sharpening is necessary.
When to Replace
Replace blades when sharpening no longer improves performance. Worn-out blades can damage the material and pose safety risks. Purchase high-quality replacement blades for better results. Regularly replacing blades keeps the copper cutting tool efficient and safe to use.
Effective use of copper cutting tools ensures clean and precise cuts. Mastering the art of copper cutting is essential for any plumber or DIY enthusiast working with copper pipes and tubing. Practicing and adhering to safety guidelines will enhance skill and prevent accidents. Proper tool usage offers numerous benefits, including seamless plumbing installations and extended tool longevity. Regular maintenance and care of cutting tools will ensure they serve well for years to come. Precision in copper cutting remains key to success in the world of plumbing.
See Also
Scooter Upgrades: High-Quality Parts for Optimal Performance
Winter Warmth: Cozy Socks and Towels for Ultimate Comfort
Diverse Selection: Men’s and Women’s Socks for Every Style
